|
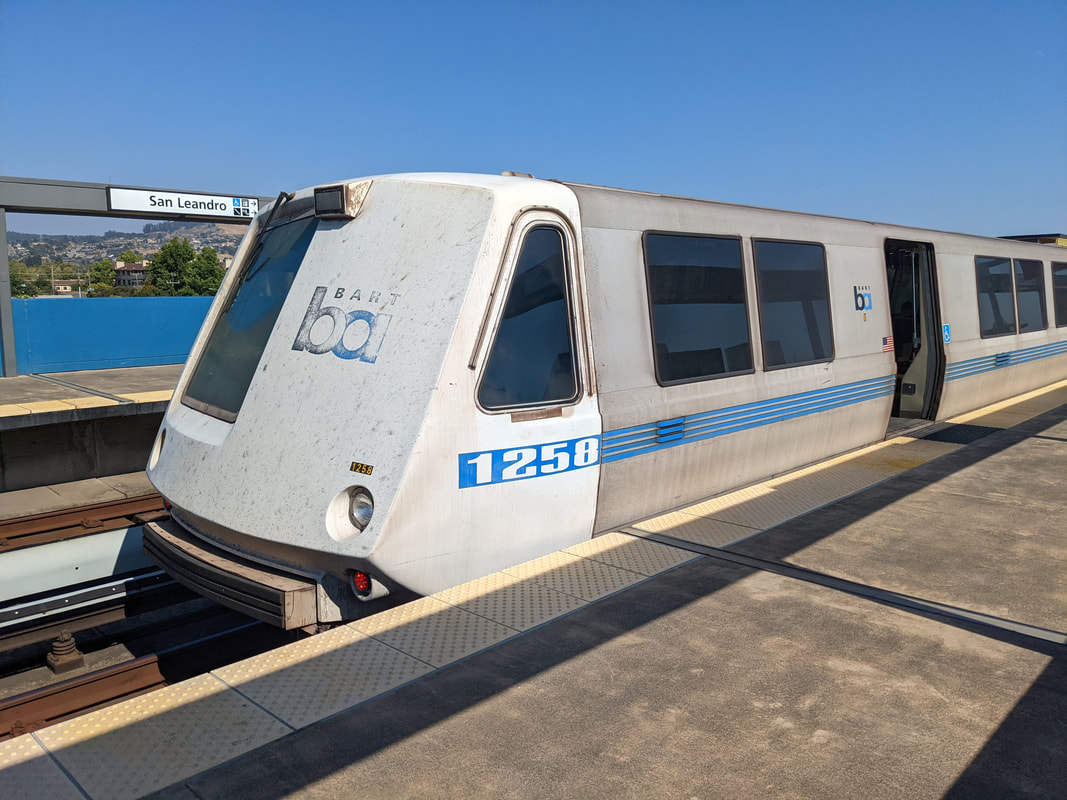
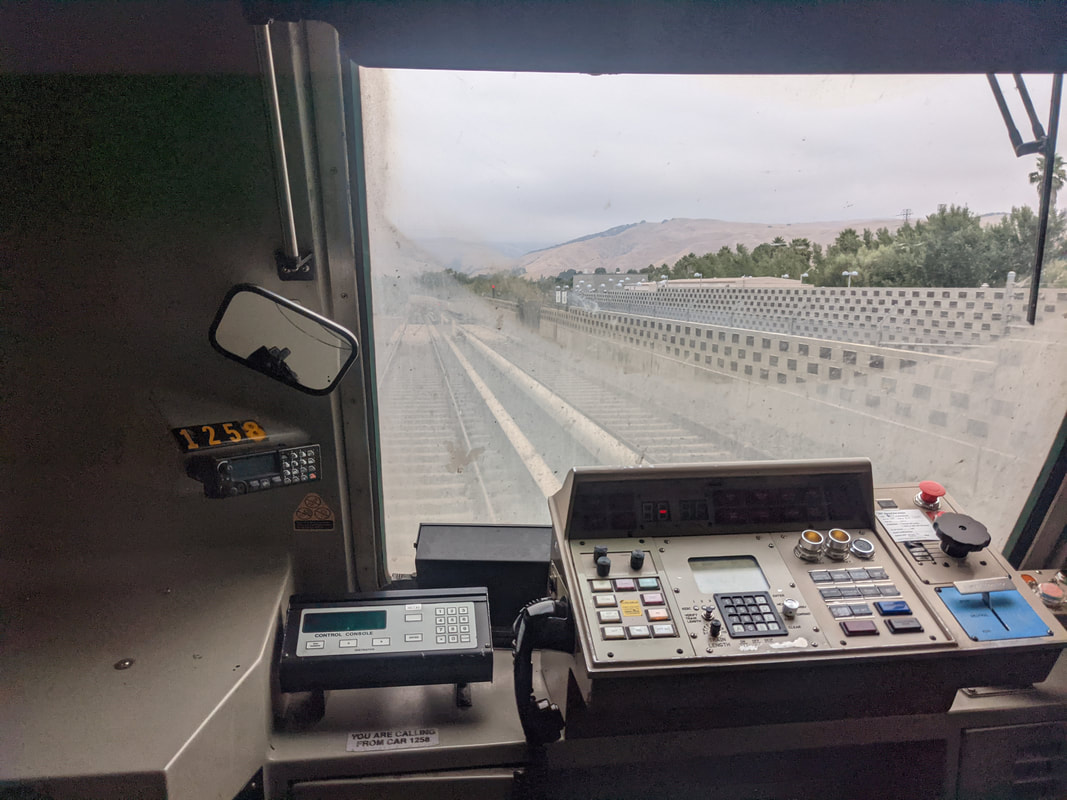
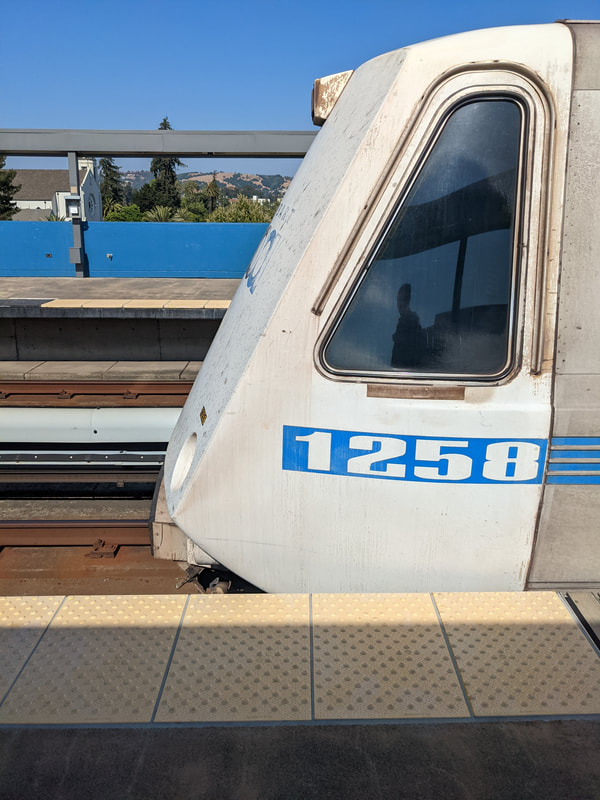
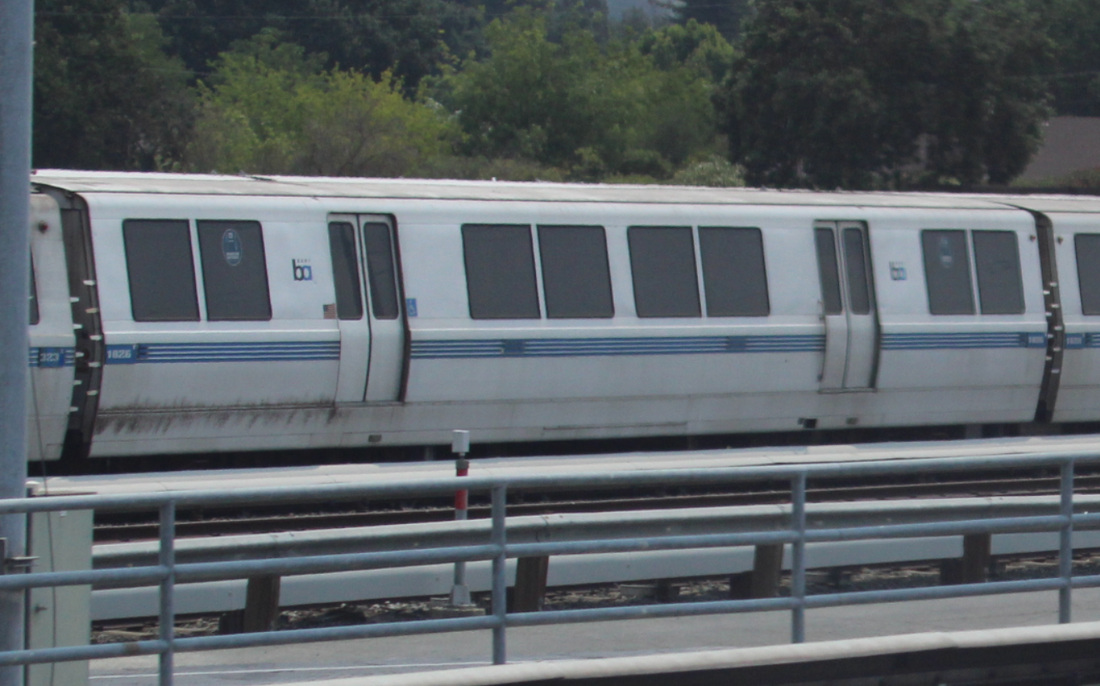
Let's take a look at another random A2 car - this time, the old 1258.
Originally built as A car 258 in 1975, by Rohr, and delivered to BART on June 18, 1975. Things were so bad back then that the final A cars, including 258, were delivered without carborne ATC equipment - they were essentially mothballed right out of the factory. Like many other late A cars, the 258 lost her motors and didn't enter service till the late 1970s. She was rebuily into A2 car 1258 in 2002 by Bombardier, and 21 years later is still rolling around the system on Orange and Red line trains. She has a little patch below the left cab window.
1 Comment
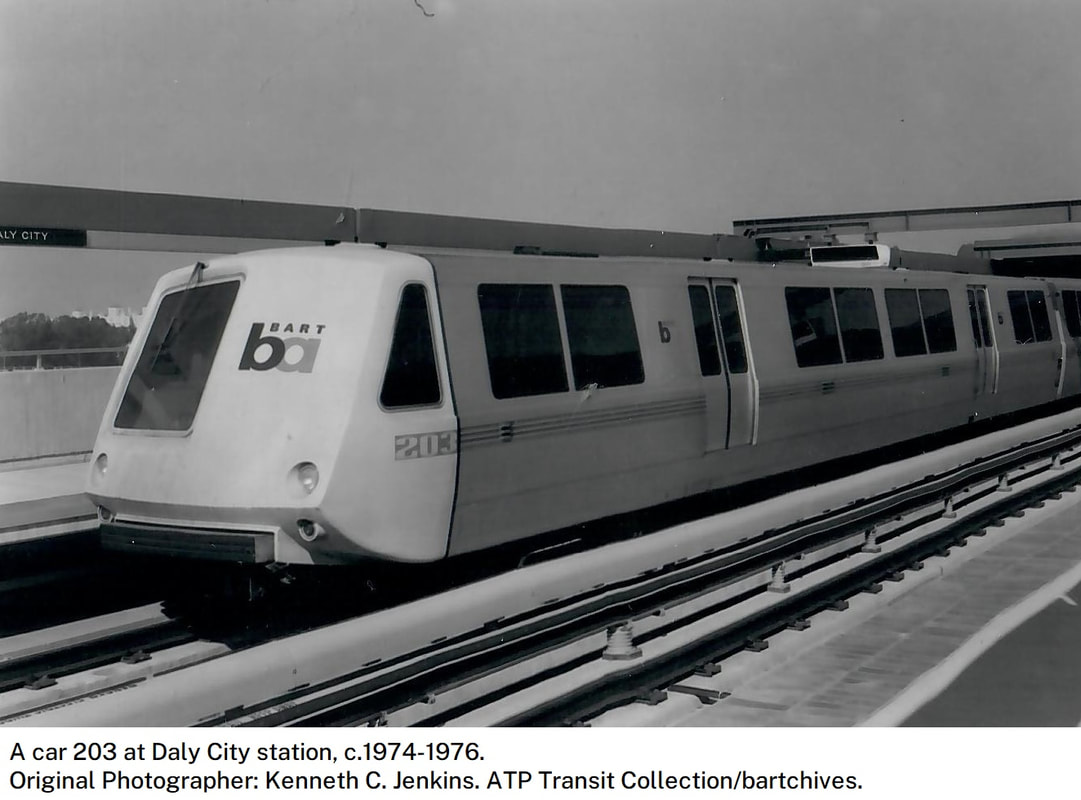
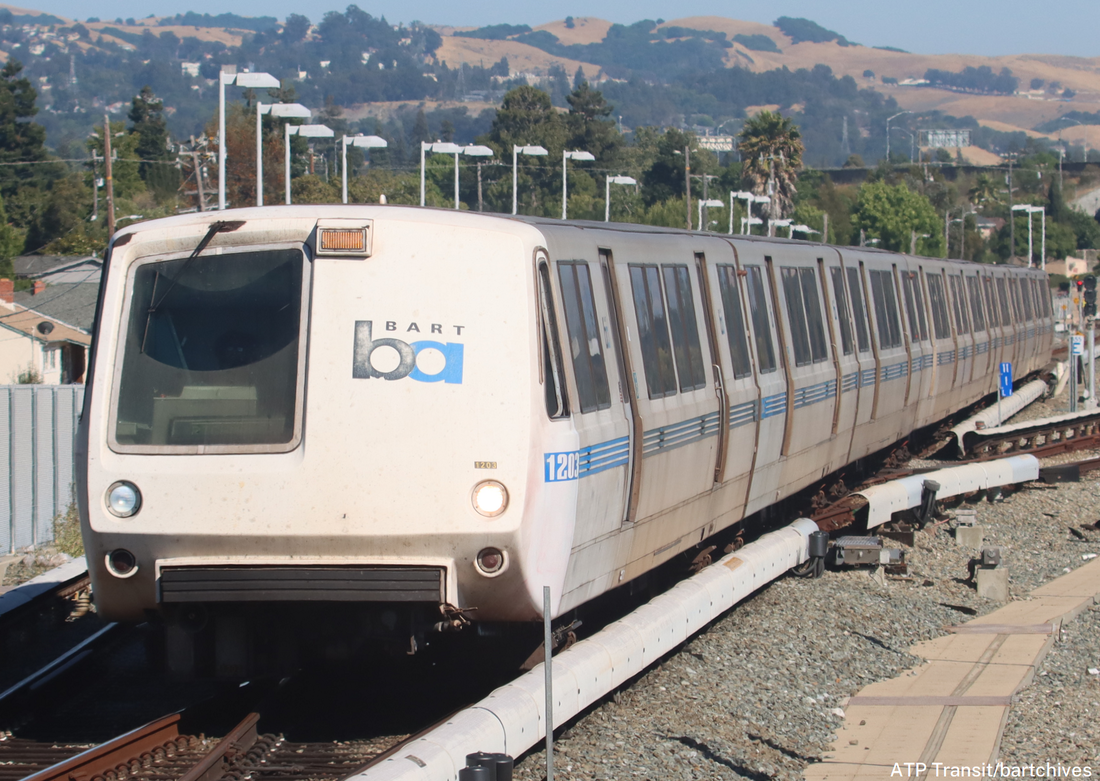
This year, the oldest A (technically, A2) cars reach the 50-year mark - a half century since their original construction. One such example is A2 car 1203, originally built by Rohr as A car 203. To note, A2 cars 1164-1250 were built in 1973 and 1251-1276 were built in 1975.
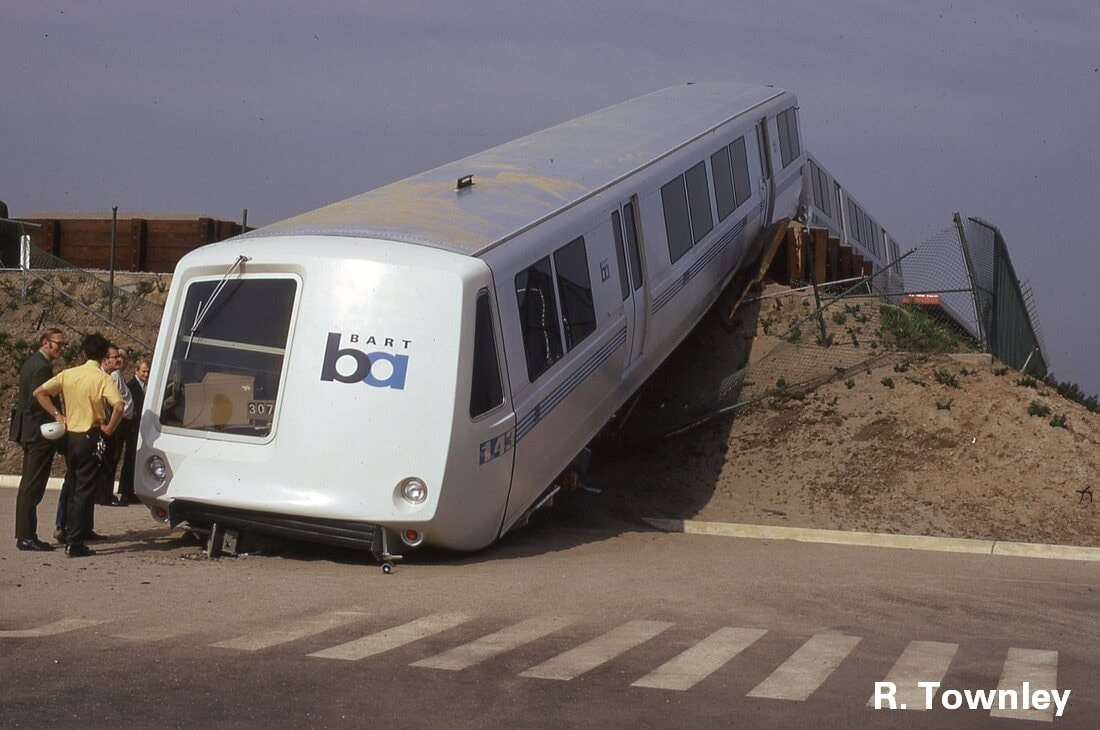
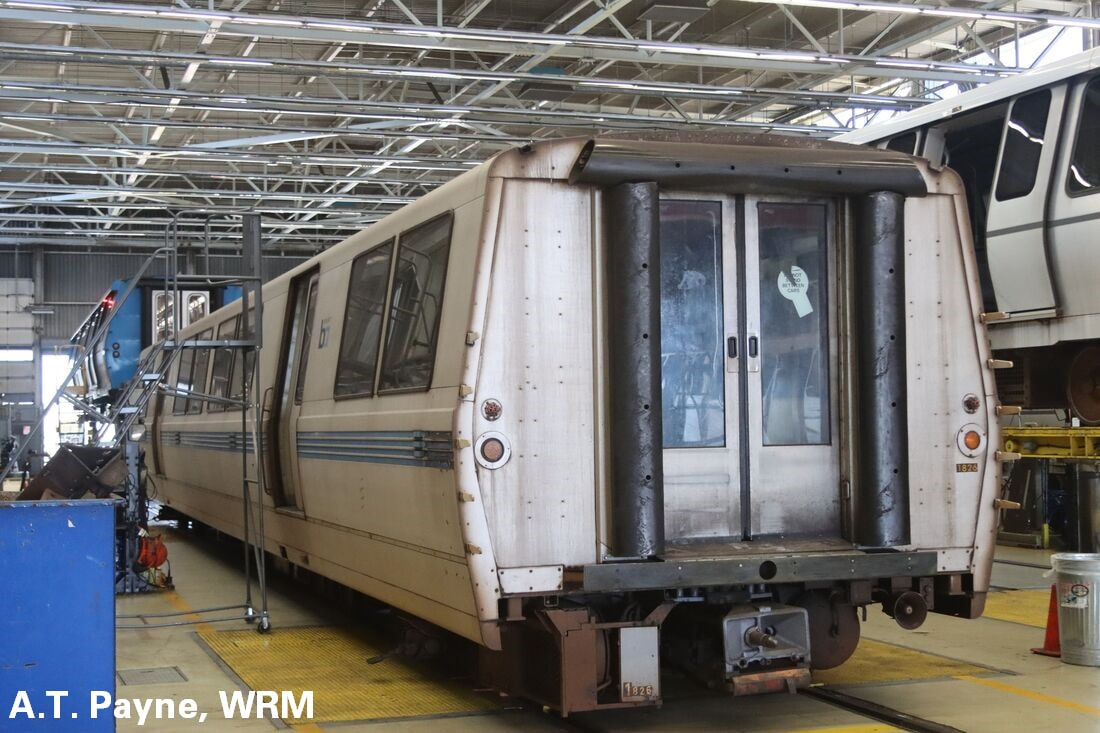
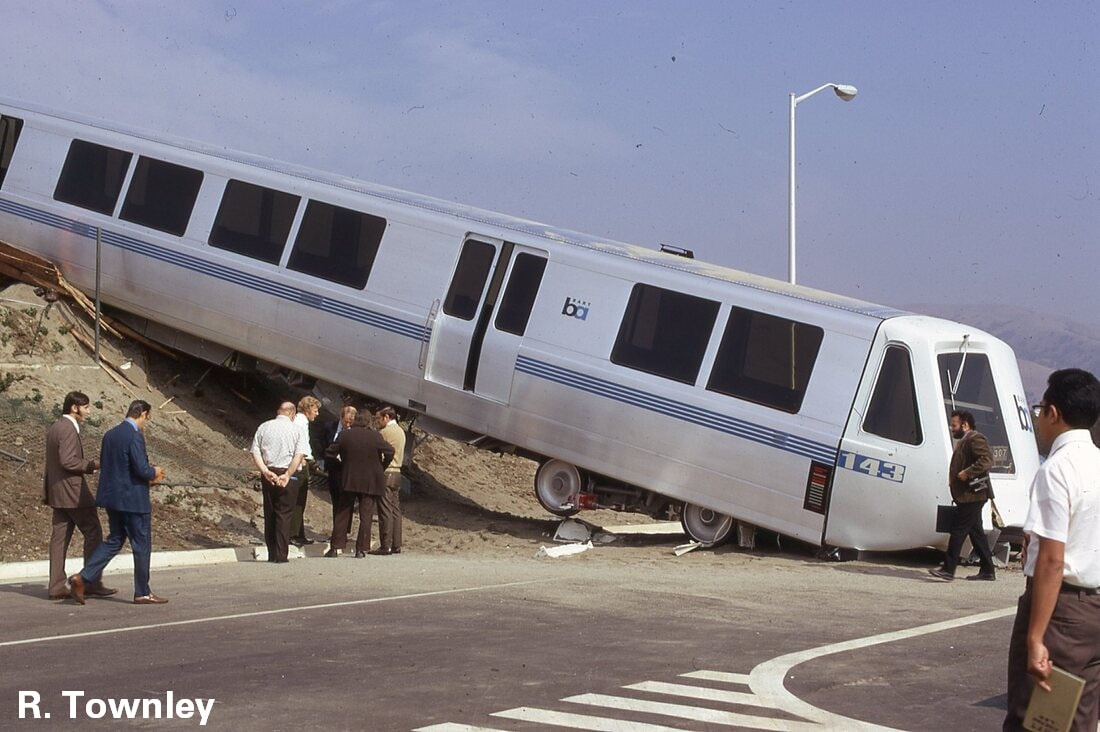
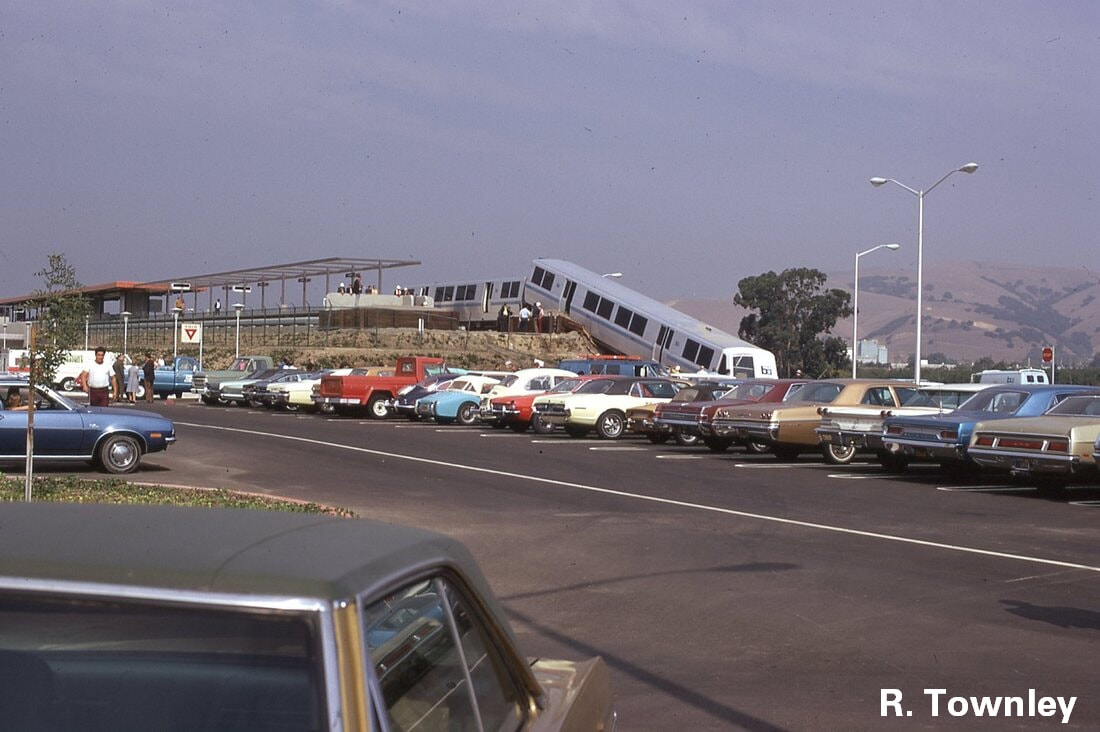
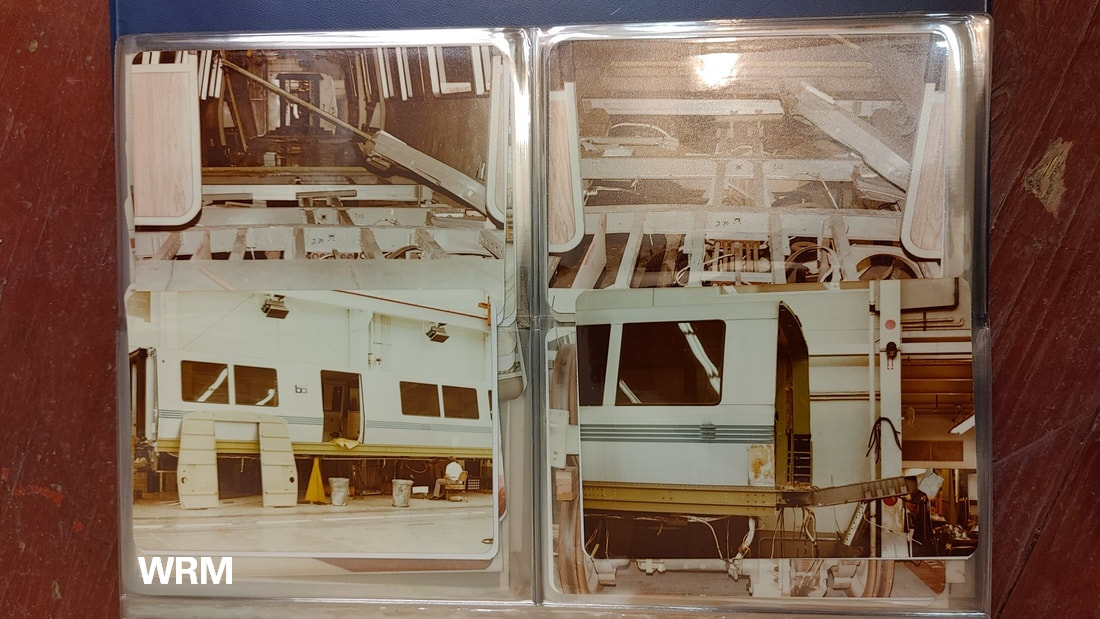
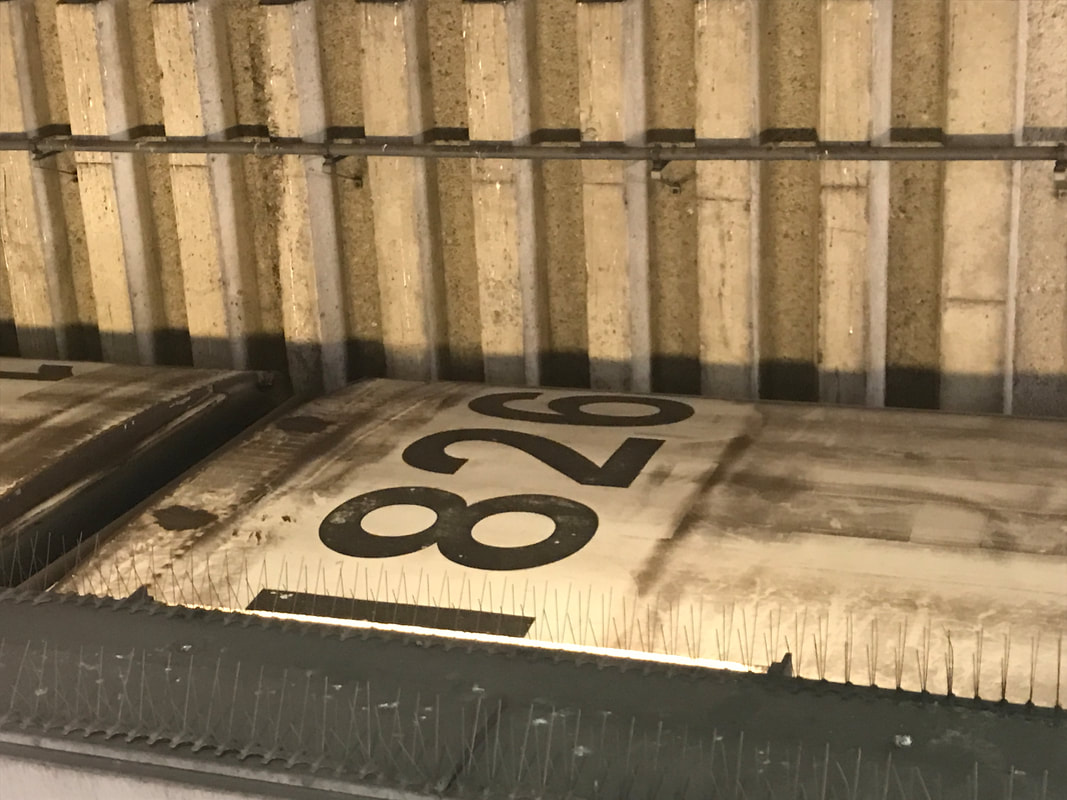
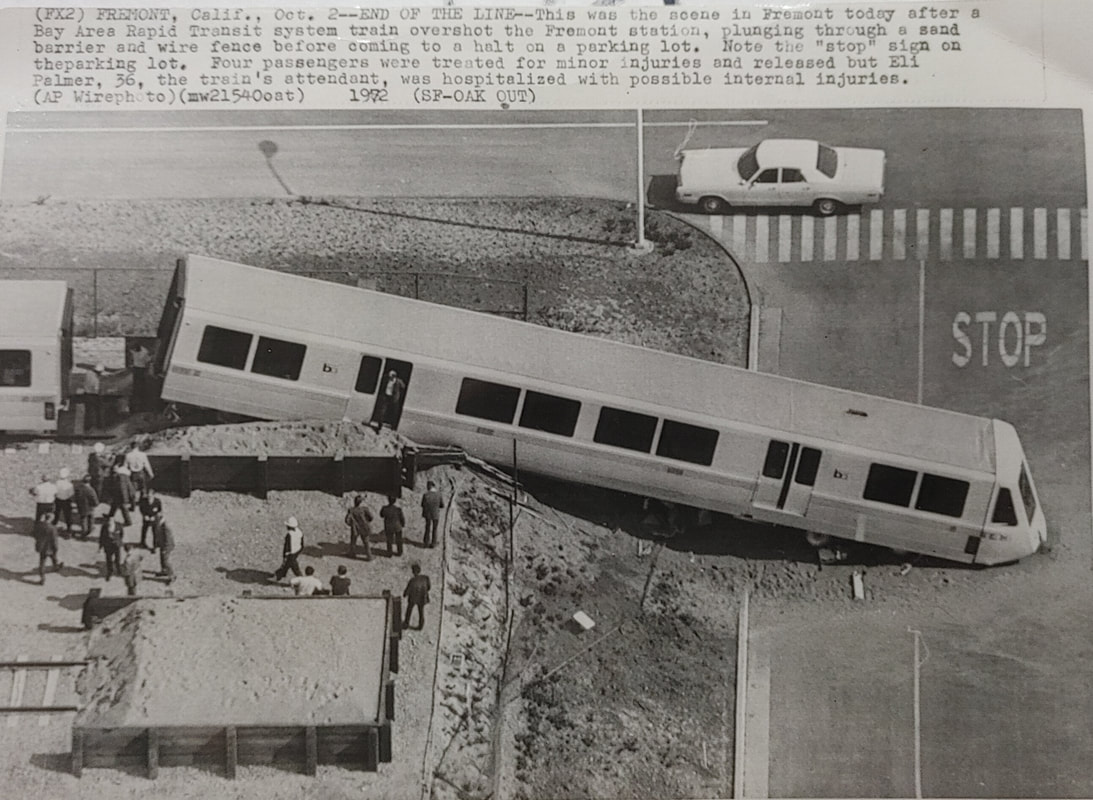
The first order for BART revenue vehicles consisted of 250 cars - 150 A cars and 100 B cars. The 203 was built within this order, and about the 156th car off the assembly line. It was delivered to BART in March 1973 and entered service within the year. Further orders for cars resulted in a fleet sized to be 176 A cars and 274 B cars (but never totally achieved). By the 1990s, the A/B cars were a bit long in the tooth and in need of a rebuilding. The midlife refurbishment program included the rebuilding of A car 203 into A2 car 1203 in 2001. Now, about 22 years and 2.2 million miles later, the legacy fleet is steadily being replaced by the Fleet of the Future. The 1203 will probably meet its end thorough scrapping, or it may be among the chosen few BART cars to find a second (or perhaps third) life in an alternative use. Whatever the case, here are a couple pics of a “young” 203 in the 1970s and an “old” 1203 in 2023 – the former from my collection and the latter taken this month (with a dead headlight nonetheless). (To note, A cars in service in 1972 are all now B2 cars numbered in the 1800s-1900s, leaving the oldest A2 car as the 1164, delivered in January 1973). Side note: The story of the BART legacy cars is not one which can be shortened to a series of posts here and crossposted in other places. I am working on a book covering the history of the BART fleet, from design to retirement, and it is fast approaching 400 pages chocked full of detail and pictures. What would you like to see in such a book and how would you gauge interest in such a subject? Please feel free to contact me on the "about" page of the website. Thanks! Today marks the final chapter of one of BART’s most historic Legacy Cars: the Fremont Flyer. The Fremont Flyer was originally known as A car 143, the 48th car off of the Rohr assembly line in Chula Vista, CA. The car was delivered to Hayward Yard on August 31, 1972, less than two weeks ahead of BART’s opening day, and underwent testing to ensure the car was ready for revenue service – or so it was thought. The shiny new 143 entered revenue service on October 2, 1972, filling in for two broken down trains. Dispatched as Train 307, a short two car train with A cars 143 and A car 118 – the latter was a “Day One veteran” – headed south from Hayward Yard to Fremont station (143 leading), thence to MacArthur (118 leading), the northern terminus at the time. Train 307 then headed south to Fremont. While approaching the A85 interlocking just north of Fremont station, the train received a 27-mph speed code – one of eight discreet speed codes on the BART ATC system – to ensure the train would safely cross over from track 1 to track 2 and stop within the platform. Unbeknownst to anyone on the train, a tiny yet faulty crystal, controlling an oscillator on a printed circuit board, incorrectly decoded the speed code to mean the train should speed up to almost 70 mph – which it achieved. Crossing over the A85 interlocking at 66 mph, the train attendant recognized something was amiss and did all that was possible to stop the train (including pressing the stop button so hard he broke the mounting and pushed it through the console). Even then, the braking was inadequate; the train sped through the center of platform 2 at 42-50 mph and impacted the sandpile at about 26-33 mph (sources debate speeds), continued and landed in the parking lot – short of a stop sign. Injured riders and the train attendant were rushed to the nearby Washington Hospital. The accident brought national attention to the safety of BART, alongside significant changes to carborne ATC equipment and changes across the system. Such changes included, but were not limited to, additional circuitry to ensure the decoding of the correct speed code, alongside the addition of wayside markers showing where a train should start braking and the maximum speed. Years of revisions and refinement to the ATC system following the Fremont Flyer incident has made BART a safer system for all who ride it. A car 143 never carried another paying rider but it found a new life as a B car. In fact, the damage was severe enough for the BART forces to recommend salvaging parts and scrapping the car. Fortunately, BART engineering know-how was on its side and the 143 was repairs and converted into B car 826 by Hayward Shop forces by the end of 1981. It then rolled again, this time as a standard B car for about 20 years. As part of the A and B car refurbishment of the A and B cars during the turn of the century, B car 826 was rebuilt and renumbered into B2 car 1826. In its final years, it was assigned to Concord yard and seen in the middle of long Yellow line trains. After this major incident, but then a successful repair and conversion, old 143 carried thousands of passengers millions of miles. BART is currently replacing their Legacy Cars with the Fleet of the Future cars. The Fremont Flyer was no exception to this, and after 50 years since it first entered revenue service, this car was decommissioned. BART forces also recognized the historical importance of this car, and invited Western Railway Museum volunteers to preserve artifacts from this car for posterity and for use in the future Rapid Transit History Center. WRM volunteers were able to identify the Y end (once cab end) exterior and interior number plates, the ADtranz rebuilding plate (c. 2001), and a seat. These artifacts will help tell us tell the story of one of the most historic transit vehicles of the BART legacy fleet. This article was written by ATP Transit for the Western Railway Museum.
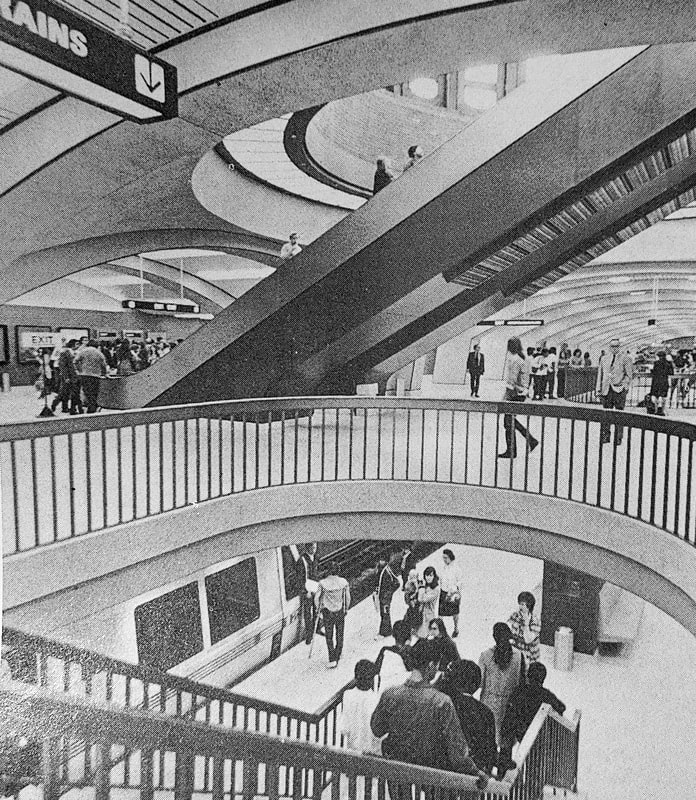
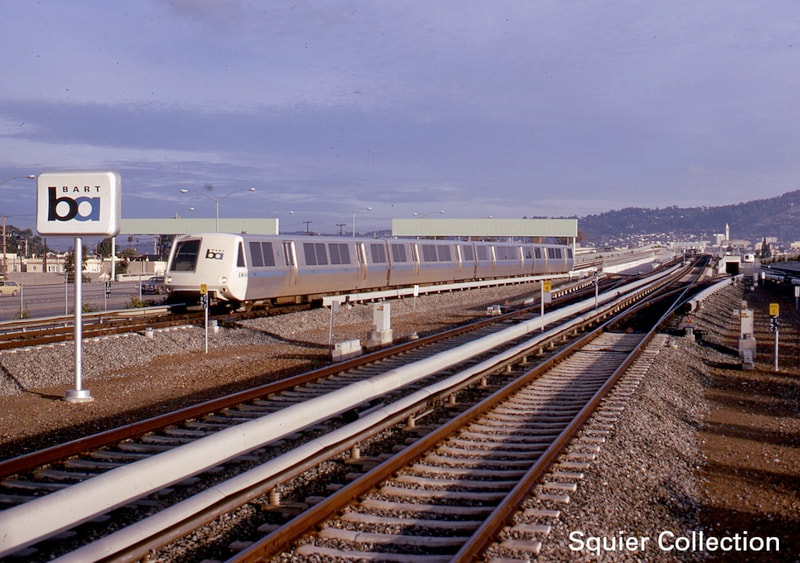
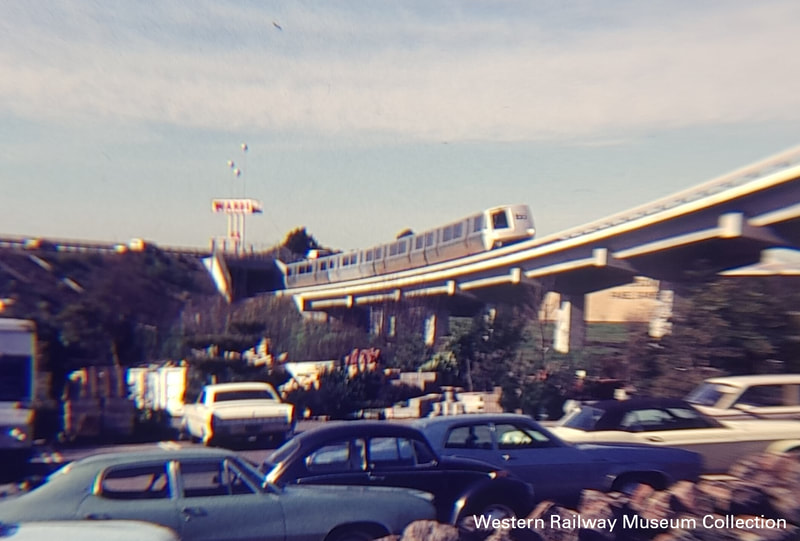
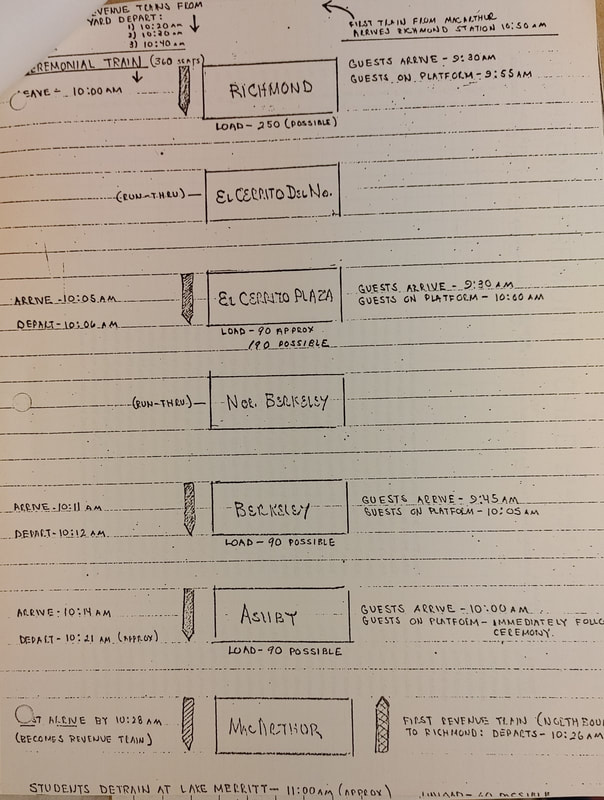
Fifty years ago today (1/29/1973), the R line (MacArthur to Richmond) opened for revenue service. Here are some pictures of the line around the time it opened, and some pictures of the station plaques and art.
This was the second segment of the BART system to open, after the A and K lines (MacArthur to Fremont) on September 11, 1972. Photo gallery: click on the thumbnails to view the full size images. |
About
"The Two Bagger" is meant to be a place to store more "blog" style posts on various cars, pictures, and random tidbits/trivia. At BART, a "two bagger" is a rather informal name for a two car train. Two car trains rolled in revenue service back in 1972. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|






























 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
